Unveiling the Power-Packed Ingredients of Magnesium Gummies: A Comprehensive Review
In the realm of dietary supplements, the market is flooded with numerous options, each promising a plethora of health benefits. Among these, Magnesium Gummies stand out as a popular choice due to their ease of consumption and potential health advantages. However, not all magnesium supplements are created equal. Today, we delve into the intricacies of Magnesium Gummies 1000mg, enriched with essential nutrients like Magnesium Citrate, Vitamin D, B6, CoQ10, and Calcium, offering a comprehensive blend designed to support overall health and well-being.
Understanding the Ingredients:
- Magnesium is an essential mineral involved in over 300 biochemical reactions in the body, ranging from energy production to muscle function and nervous system regulation.
- Magnesium Citrate is a highly bioavailable form of magnesium, meaning it is easily absorbed and utilized by the body.
- It plays a crucial role in maintaining healthy bones, supporting cardiovascular health, and regulating blood sugar levels.
- Adequate magnesium intake has also been linked to improved mood, reduced stress, and enhanced sleep quality.
Vitamin D:
- Often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” Vitamin D is crucial for calcium absorption and bone health.
- It plays a vital role in supporting the immune system, promoting cell growth and repair, and modulating inflammation.
- Many people are deficient in Vitamin D, especially those who live in regions with limited sunlight exposure or spend extended periods indoors.
Vitamin B6:
- Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin involved in various metabolic processes.
- It aids in the conversion of food into energy and supports neurotransmitter synthesis, thereby promoting cognitive function and mood regulation.
- Vitamin B6 is essential for the production of hemoglobin, which carries oxygen in red blood cells, and helps maintain a healthy immune system.
Coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10):
- CoQ10 is a powerful antioxidant naturally produced by the body and found in every cell.
- It plays a crucial role in energy production within the mitochondria, the powerhouse of cells.
- CoQ10 levels decline with age and may be depleted by certain medications or health conditions.
- Supplementation with CoQ10 can help support cardiovascular health, improve exercise performance, and protect against oxidative damage.
Calcium:
- Calcium is the most abundant mineral in the body, primarily stored in bones and teeth.
- It is essential for bone strength and density, muscle function, nerve transmission, and hormone secretion.
- Adequate calcium intake is vital throughout life, especially during childhood, adolescence, and older adulthood, to prevent osteoporosis and bone fractures.
Vitamin D
often referred to as the “sunshine vitamin,” is a crucial nutrient that offers a wide array of health benefits. Here are some of the key advantages of maintaining adequate levels of Vitamin D:
Bone Health: One of the most well-known benefits of Vitamin D is its role in promoting bone health. It aids in the absorption of calcium and phosphorus, essential minerals for building and maintaining strong bones. Sufficient Vitamin D intake helps prevent conditions like rickets in children and osteomalacia in adults, both of which are characterized by weakened or soft bones.
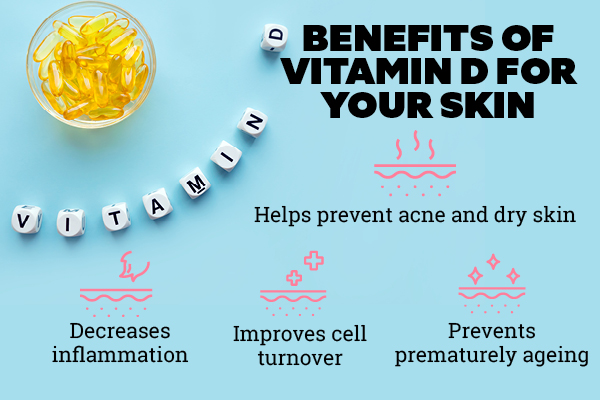
Immune Function: Vitamin D plays a vital role in supporting the immune system, helping the body defend against infections and illnesses. It enhances the function of immune cells, such as T cells and macrophages, which are involved in identifying and destroying pathogens like bacteria and viruses. Adequate Vitamin D levels have been associated with a reduced risk of respiratory infections, autoimmune diseases, and certain cancers.
Mood Regulation: There is growing evidence suggesting a link between Vitamin D and mood regulation. Low levels of Vitamin D have been associated with an increased risk of depression, seasonal affective disorder (SAD), and other mood disorders. Vitamin D receptors are present in areas of the brain involved in mood regulation, and supplementation may help improve symptoms of depression and enhance overall well-being.
Muscle Function: Vitamin D is essential for optimal muscle function and strength. It plays a role in muscle protein synthesis, nerve function, and coordination. Adequate Vitamin D levels may help reduce the risk of falls and fractures, particularly in older adults, by maintaining muscle integrity and balance.
Heart Health: Emerging research suggests that Vitamin D may have benefits for cardiovascular health. Adequate Vitamin D levels have been associated with a reduced risk of hypertension, heart disease, and stroke. Vitamin D may help regulate blood pressure, improve endothelial function (the health of blood vessels), and reduce inflammation, all of which contribute to a healthier cardiovascular system.
Cancer Prevention: Some studies have suggested a potential link between Vitamin D status and cancer risk reduction. Adequate Vitamin D levels may help lower the risk of certain cancers, including breast, prostate, colon, and pancreatic cancer. Vitamin D may exert anticancer effects by regulating cell growth, differentiation, and apoptosis (cell death), as well as by modulating immune function and inflammation.
Brain Health: Vitamin D receptors are abundant in the brain, indicating its importance for neurological function. Adequate Vitamin D levels have been associated with a lower risk of cognitive decline, dementia, and Alzheimer’s disease. Vitamin D may exert neuroprotective effects by reducing inflammation, promoting neuronal survival, and enhancing synaptic function.
Pregnancy and Fetal Development: Vitamin D plays a crucial role in pregnancy and fetal development. Adequate Vitamin D levels are essential for maternal bone health, fetal skeletal development, and overall pregnancy outcomes. Vitamin D deficiency during pregnancy has been linked to an increased risk of pre-eclampsia, gestational diabetes, preterm birth, and low birth weight.
Vitamin B6
Vitamin B6, also known as pyridoxine, is a water-soluble vitamin that plays a crucial role in numerous biochemical reactions throughout the body. Here are some of the key benefits of Vitamin B6:
Energy Metabolism: Vitamin B6 is essential for the metabolism of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats. It acts as a coenzyme in various enzymatic reactions involved in breaking down these macronutrients into usable forms of energy. Adequate Vitamin B6 levels are necessary for maintaining energy production and supporting overall vitality.
Neurotransmitter Synthesis: Vitamin B6 is involved in the synthesis of neurotransmitters, such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA). These neurotransmitters play crucial roles in mood regulation, cognitive function, and stress response. Adequate Vitamin B6 levels are necessary for optimal brain health and emotional well-being.
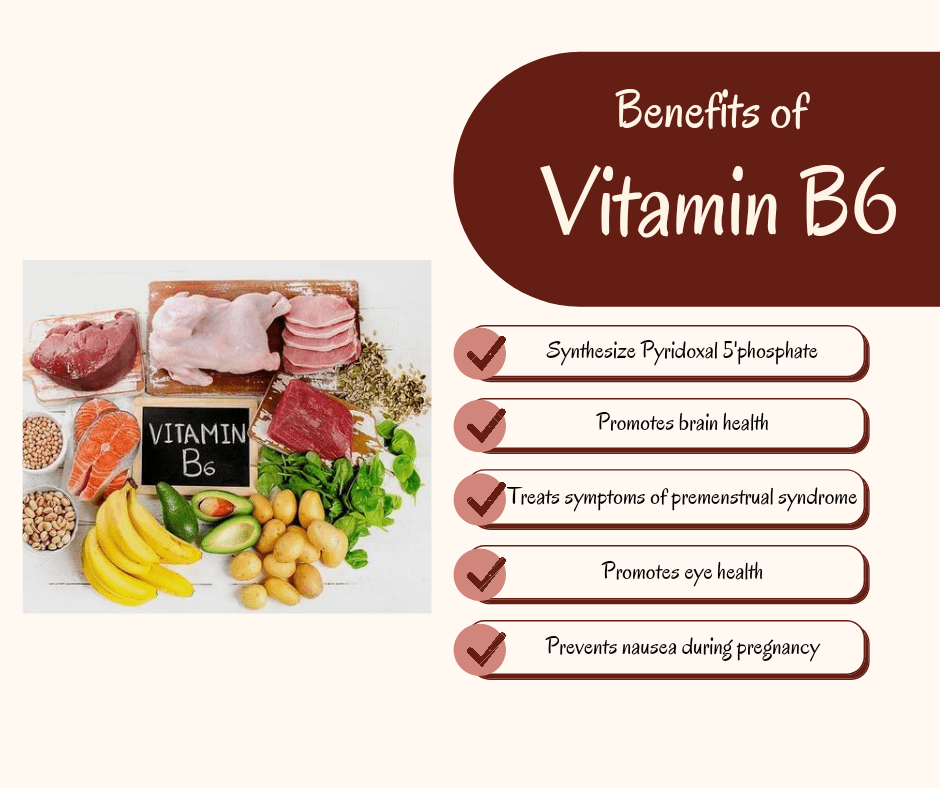
Hemoglobin Formation: Vitamin B6 is involved in the synthesis of hemoglobin, the protein in red blood cells that carries oxygen from the lungs to tissues throughout the body. Adequate Vitamin B6 levels are necessary for the production of healthy red blood cells and the prevention of anemia.
Immune Function: Vitamin B6 plays a role in supporting the immune system by modulating immune cell activity and antibody production. It helps regulate the function of lymphocytes, white blood cells involved in immune response, and enhances the body’s ability to fight infections and diseases.
Cardiovascular Health: Vitamin B6 may help maintain cardiovascular health by regulating homocysteine levels in the blood. Elevated levels of homocysteine are associated with an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. Vitamin B6, along with other B vitamins, helps convert homocysteine into other beneficial compounds, thereby reducing cardiovascular risk.
Prenatal Health: Adequate Vitamin B6 intake is crucial during pregnancy for both maternal and fetal health. Vitamin B6 plays a role in fetal brain development and may help alleviate symptoms of nausea and vomiting commonly experienced during pregnancy (morning sickness). It also supports the formation of red blood cells in both the mother and the developing fetus.
Skin Health: Vitamin B6 may contribute to healthy skin by supporting collagen formation and promoting wound healing. Collagen is the main structural protein in the skin, responsible for its strength, elasticity, and integrity. Adequate Vitamin B6 levels are necessary for maintaining skin health and preventing conditions like dermatitis and eczema.
Hormone Regulation: Vitamin B6 is involved in the synthesis and metabolism of various hormones, including estrogen, progesterone, and testosterone. It helps regulate hormone levels and may alleviate symptoms of hormone-related conditions such as PMS (premenstrual syndrome) and menopausal symptoms.
In conclusion, Vitamin B6 is a vital nutrient with diverse roles in energy metabolism, neurotransmitter synthesis, hemoglobin formation, immune function, cardiovascular health, prenatal health, skin health, and hormone regulation. Ensuring an adequate intake of Vitamin B6 through dietary sources or supplementation can support overall health and well-being. However, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplementation regimen, especially if you have underlying health conditions or are taking medications.


